-
Research Article
-
Analysis of BEMS Applicability in Existing Multi-family Housing Based on Facility and Communication Infrastructure
기축 공동주택의 설비 및 통신 인프라 구축 현황에 따른 BEMS 적용성 분석
-
Young-Ae Lee, Byung Chang Kwag, Hyemin Ha, Gil-Tae Kim
이영애, 곽병창, 하혜민, 김길태
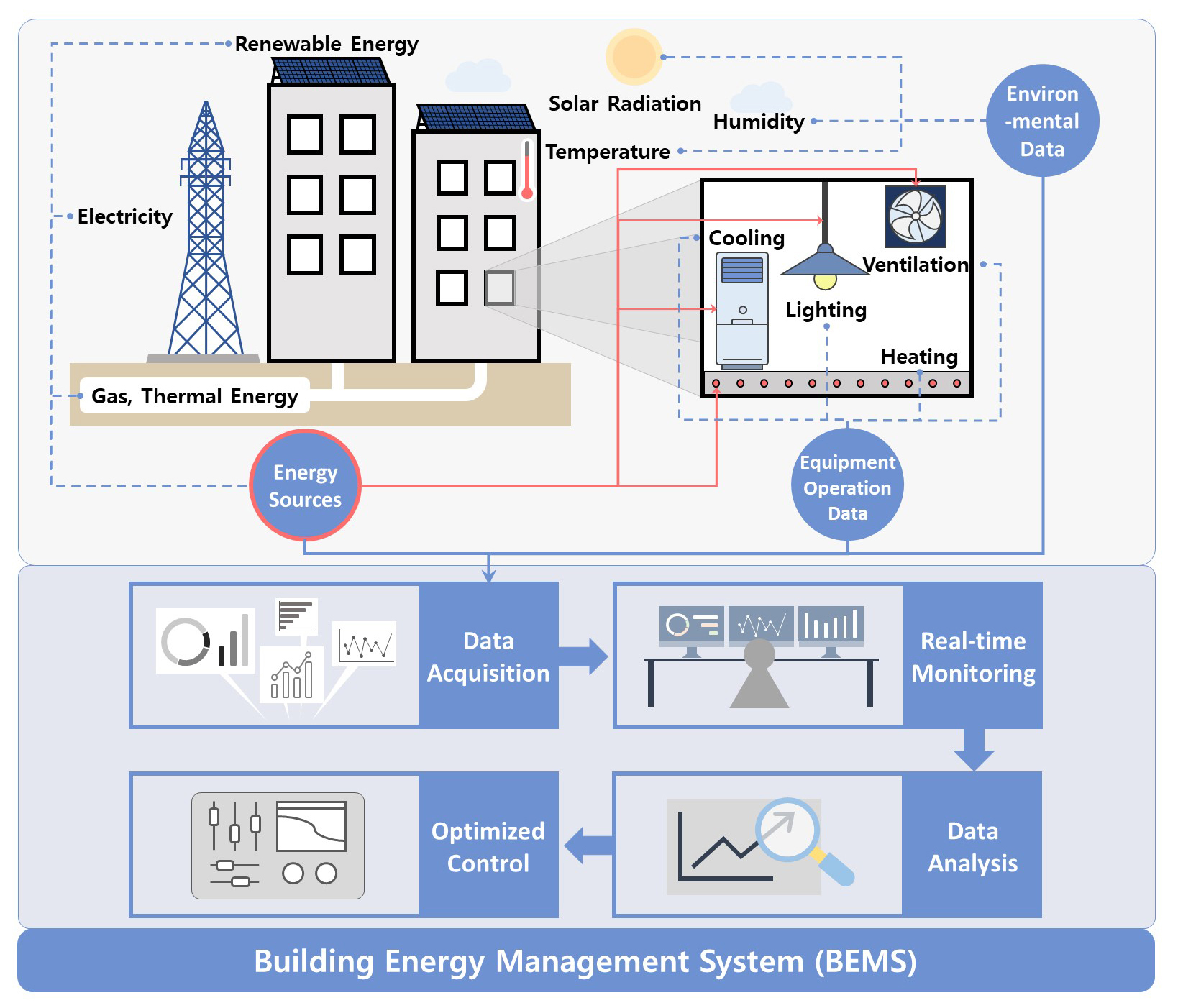
- This study analyzes the applicability of Building Energy Management Systems (BEMS) in existing multi-family housing in Korea, based on facility and communication …
- This study analyzes the applicability of Building Energy Management Systems (BEMS) in existing multi-family housing in Korea, based on facility and communication infrastructure conditions by year of project and occupancy approval. A total of 300 apartment complexes supplied by the Korea Land and Housing Corporation (LH), received occupancy approval between 1990 and 2024, were examined for heating and ventilation system controllability, remote metering, and in-unit home network infrastructure. The analysis revealed distinct infrastructure characteristics according to the year of project and occupancy approval. Based on these findings, the study evaluates the feasibility and limitations of BEMS implementation in aging apartment buildings and proposes a phased strategy for practical deployment. The results provide a procedure for adopting BEMS in existing housing stock, bridging the gap between current building conditions and advanced energy management technologies. This research contributes to sustainable residential management by offering both academic insights and practical guidance for effective BEMS integration in Korea’s aging public housing sector. - COLLAPSE
-
Analysis of BEMS Applicability in Existing Multi-family Housing Based on Facility and Communication Infrastructure
-
Research Article
-
Deriving Improvement Elements of Speech Announcements in Subway Stations through a Survey for Elderly and Young Adults
고령자 및 청년자 대상 설문조사를 통한 지하철 역사 음성 안내음의 개선요소 도출
-
Hansol Song, Jongkwan Ryu
송한솔, 류종관
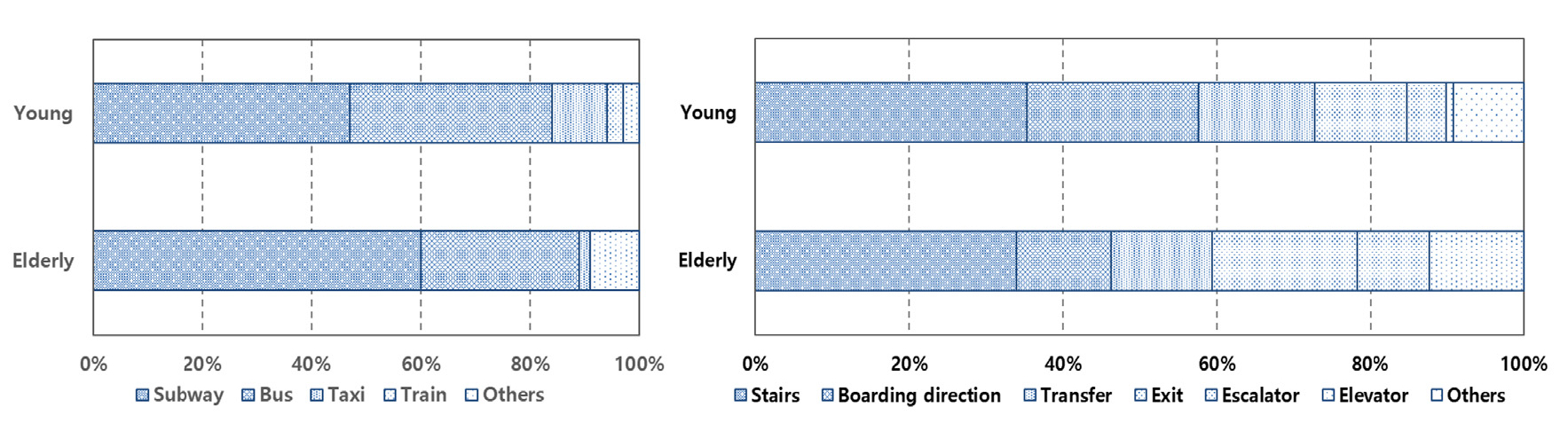
- This study aims to investigate the current status and user perception of speech announcements in subway stations to improve mobility convenience for …
- This study aims to investigate the current status and user perception of speech announcements in subway stations to improve mobility convenience for elderly people, whose importance is increasing with the entry into an aging society, and to derive characteristics of speech announcements for elderly people through comparison with a younger group. For this purpose, a survey was conducted in Seoul and the metropolitan area targeting 84 elderly people (aged 60 and above) and 138 young people (aged 19 to under 39). The questionnaire was composed of 5-point scales covering general information, physical abilities, auditory and visual capabilities, subway usage status, acoustic environment of subway stations, and experience and perception of speech announcements. The research results showed that elderly people had lower satisfaction with the acoustic environment of subway stations (noise and reverberation in platform and concourse) compared to young people, and showed differences in importantly recognizing speed and intelligibility as dissatisfaction factors of speech announcements. Both groups responded that improvement of noise in subway station was most needed for speech announcement. In particular, the main influencing factors for elderly person’s intelligibility of speech announcements were noise in space and loudness of speech announcement. The results of this study are expected to be utilized as basic data for establishing standards for speech announcement in subway station that consider the auditory and cognitive characteristics of elderly people. - COLLAPSE
-
Deriving Improvement Elements of Speech Announcements in Subway Stations through a Survey for Elderly and Young Adults
-
Research Article
-
A Review of Technical Trends and Applications of Extremum Seeking Control for Building HVAC Systems
건물 HVAC 시스템에서 극값 탐색 제어 기법의 기술적 동향 및 적용 사례 분석
-
Jong-Man Lee, Kwang-Ho Lee
이종만, 이광호
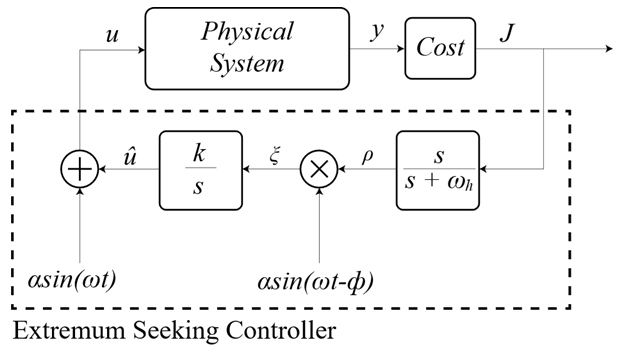
- This study comprehensively reviews technical trends and applications of Extremum Seeking Control (ESC) for enhancing the efficiency of energy-intensive building Heating, Ventilation, …
- This study comprehensively reviews technical trends and applications of Extremum Seeking Control (ESC) for enhancing the efficiency of energy-intensive building Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems. ESC offers a model-free, real-time optimization alternative to traditional control strategies. We examine ESC's fundamental principles and its algorithmic progression from single-variable methods to advanced multi- variable, Newton-based, input-output correlation (IOC ESC), and decentralized approaches, alongside practical considerations like anti-windup techniques. Literature review confirms ESC's effectiveness in achieving significant energy savings and performance gains in various HVAC applications, encompassing multi-unit systems (Variable Refrigerant Flow, Rooftop Unit) and sophisticated heat pumps (CO2, high-temperature). Notable results include a 52% COP increase for room air conditioners, 48% energy savings for mini-split systems, and a 7.7% COP improvement for CO2 heat pumps. ESC are also being innovatively applied to tasks like model-free staging logic. These results underscore ESC's role as a potent and practical tool for optimizing complex, dynamic HVAC systems. - COLLAPSE
-
A Review of Technical Trends and Applications of Extremum Seeking Control for Building HVAC Systems
-
Research Article
-
A Field Study on the Application of Extremum-Seeking Control for Energy Optimization of a VRF System
실제 건물 VRF 시스템에 극값탐색제어 적용을 통한 에너지 저감 실증 연구
-
Jong-Man Lee, Kwang-Ho Lee
이종만, 이광호
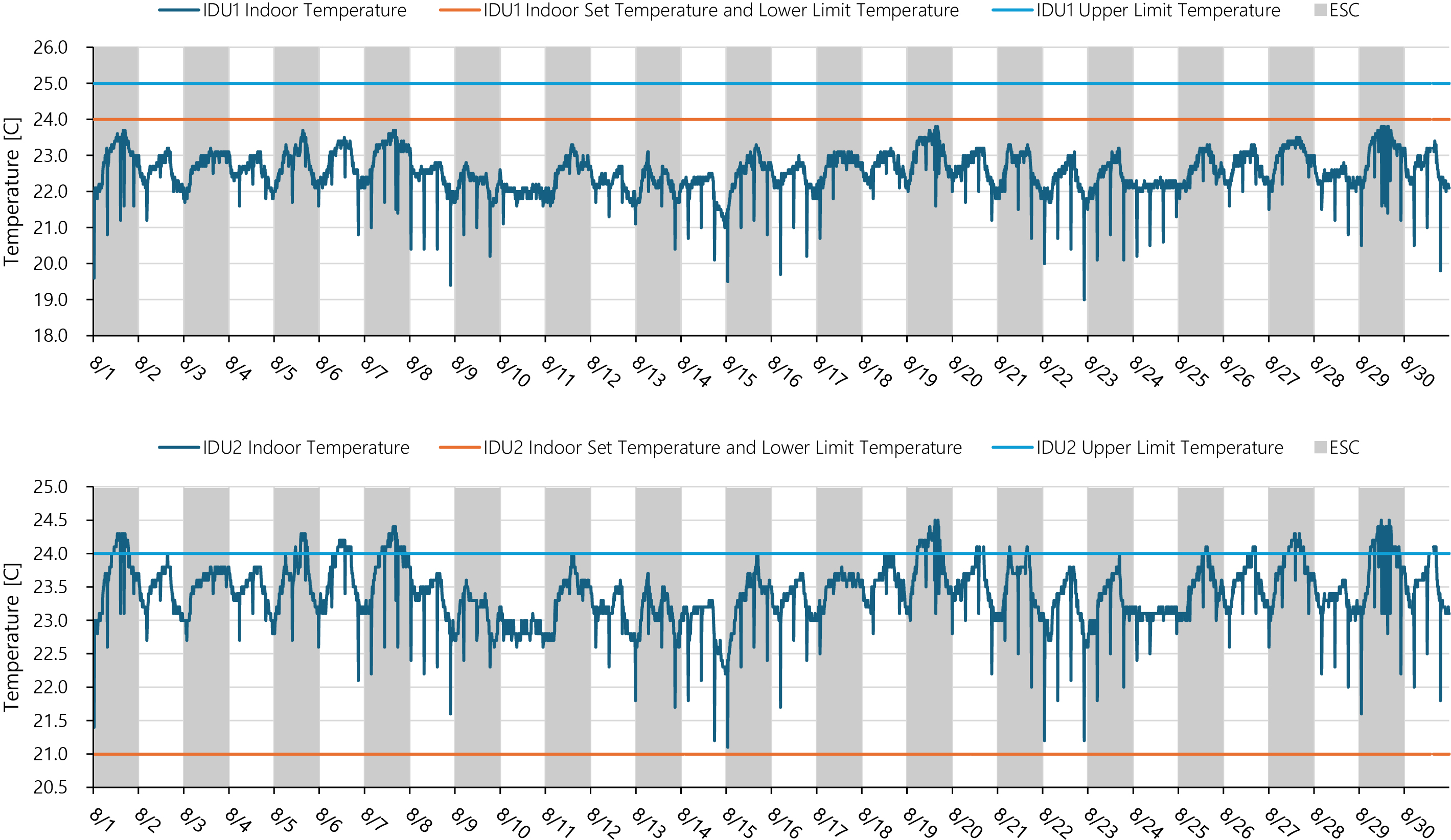
- This paper presents the development and empirical validation of an Extremum Seeking Control (ESC) algorithm applied to a Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) …
- This paper presents the development and empirical validation of an Extremum Seeking Control (ESC) algorithm applied to a Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) system in an operational building. Conventional VRF control strategies often rely on fixed setpoints for refrigerant evaporating temperature, leading to suboptimal energy efficiency, especially under part-load conditions. To address this, a model-free ESC algorithm was implemented to dynamically adjust the evaporating temperature in real-time, minimizing the total power consumption of the outdoor unit. A field test was conducted to verify the algorithm's performance. The results demonstrated that the ESC successfully optimized the system's operation, significantly improving the Coefficient of Performance (COP) across all load ranges—more than doubling it at low loads. This led to a substantial reduction in energy consumption by up to 60% in mid-load ranges. Furthermore, the analysis of indoor temperature data confirmed that these energy efficiency gains were achieved while maintaining stable and comfortable indoor thermal conditions. This study validates the practical effectiveness of ESC as a robust solution for enhancing the energy performance of VRF systems in real-world building applications. - COLLAPSE
-
A Field Study on the Application of Extremum-Seeking Control for Energy Optimization of a VRF System
-
Research Article
-
Machine Learning Based Architectural Drawing Element Extraction and Fire-Protection Design Automation: An Automated Layout Algorithm
머신러닝 기반 건축도면 요소 추출 및 소방설계 자동화: 화재방호 설비 자동 배치 알고리즘
-
Sang-Hun Yeon, Min-Gyu Kim, Doochan Choi, Kwang-Ho Lee
연상훈, 김민규, 최두찬, 이광호
- This study develops and validates an algorithm that automates fire-protection design from architectural drawings. Building-summary tables and annotations are parsed with optical …
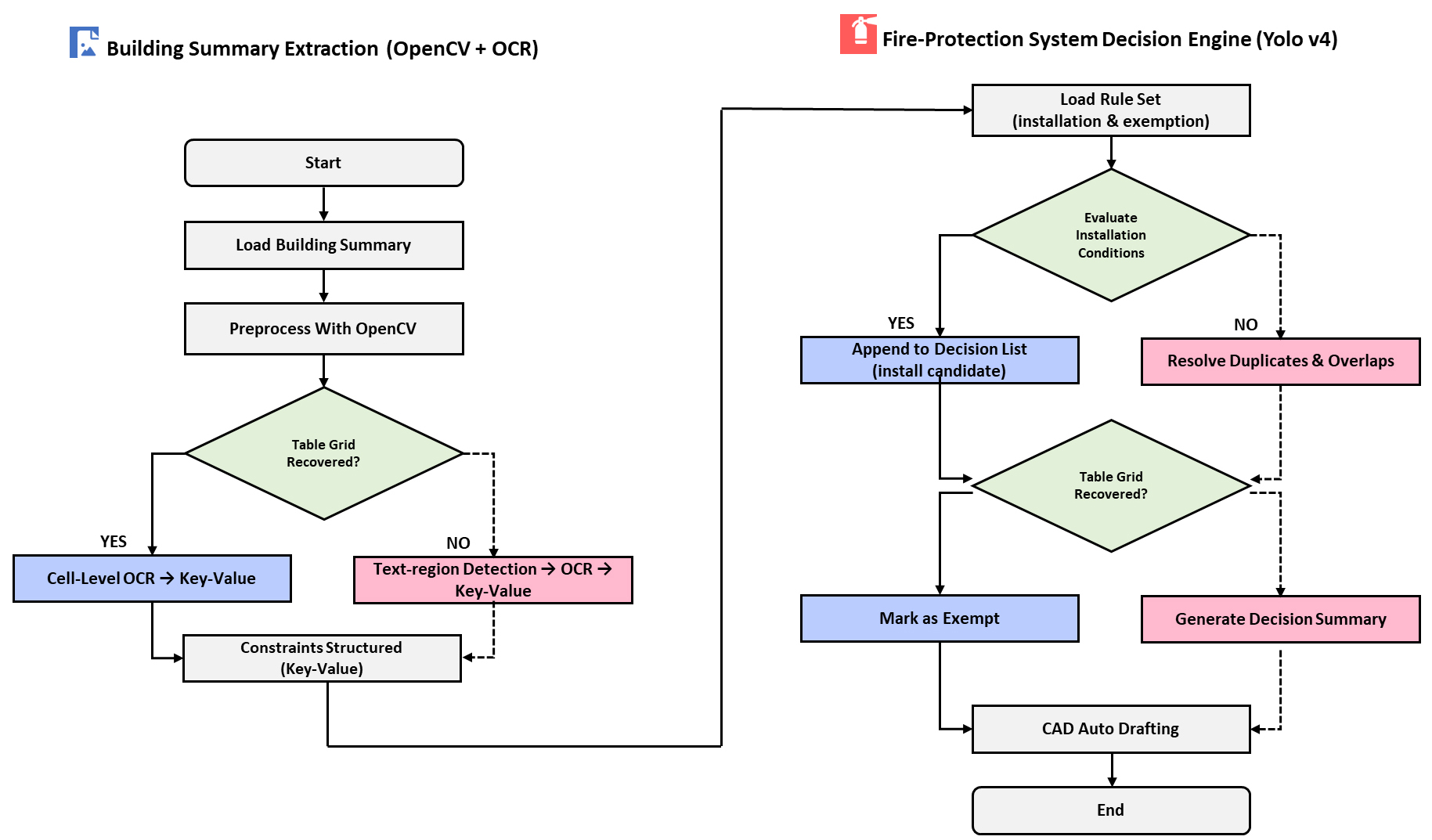
- This study develops and validates an algorithm that automates fire-protection design from architectural drawings. Building-summary tables and annotations are parsed with optical character recognition (OCR) and OpenCV to normalize occupancy, gross floor area, story count, and floor height. Doors and columns are detected by a You Only Look Once v4 (YOLO v4) convolutional neural network, and room boundaries are reconstructed to form space-level metadata. A rule engine derived from the National Fire Safety Code (NFSC) determines installation or exemption for each system and computes equipment placement and wiring. Outputs are written as computer-aided design (CAD) entities through the AutoCAD application programming interface. In tests, table structure and text recognition reached accuracy 0.91, precision 0.89, recall 0.99, F1 Score 0.94, and intersection-over-union 0.83. Average detection confidence was 0.89 for doors and 0.86–0.93 for columns. Checklist comparison yielded about 97% normal outputs, and repeated runs reproduced coordinates and connections, indicating reliable end-to-end automation from image inputs to CAD deliverables. - COLLAPSE
-
Machine Learning Based Architectural Drawing Element Extraction and Fire-Protection Design Automation: An Automated Layout Algorithm
-
Research Article
-
A Study on Improving Campus Spaces for Physical Activity using AI-Based Analysis
AI 기반 분석을 통한 신체활동 친화적 캠퍼스 공간 개선 연구
-
Miri Hwang, Eun Joo Park, Sechang Oh, Jihun Kwon, Haanbyul Baek, Minyeong Lee, Jinkyung Cho
황미리, 박은주, 오세창, 권지훈, 백한별, 이민영, 조진경
- This study aims to analyze the spatial structure of a university Athletic field and propose design improvements to enhance its utilization. A …
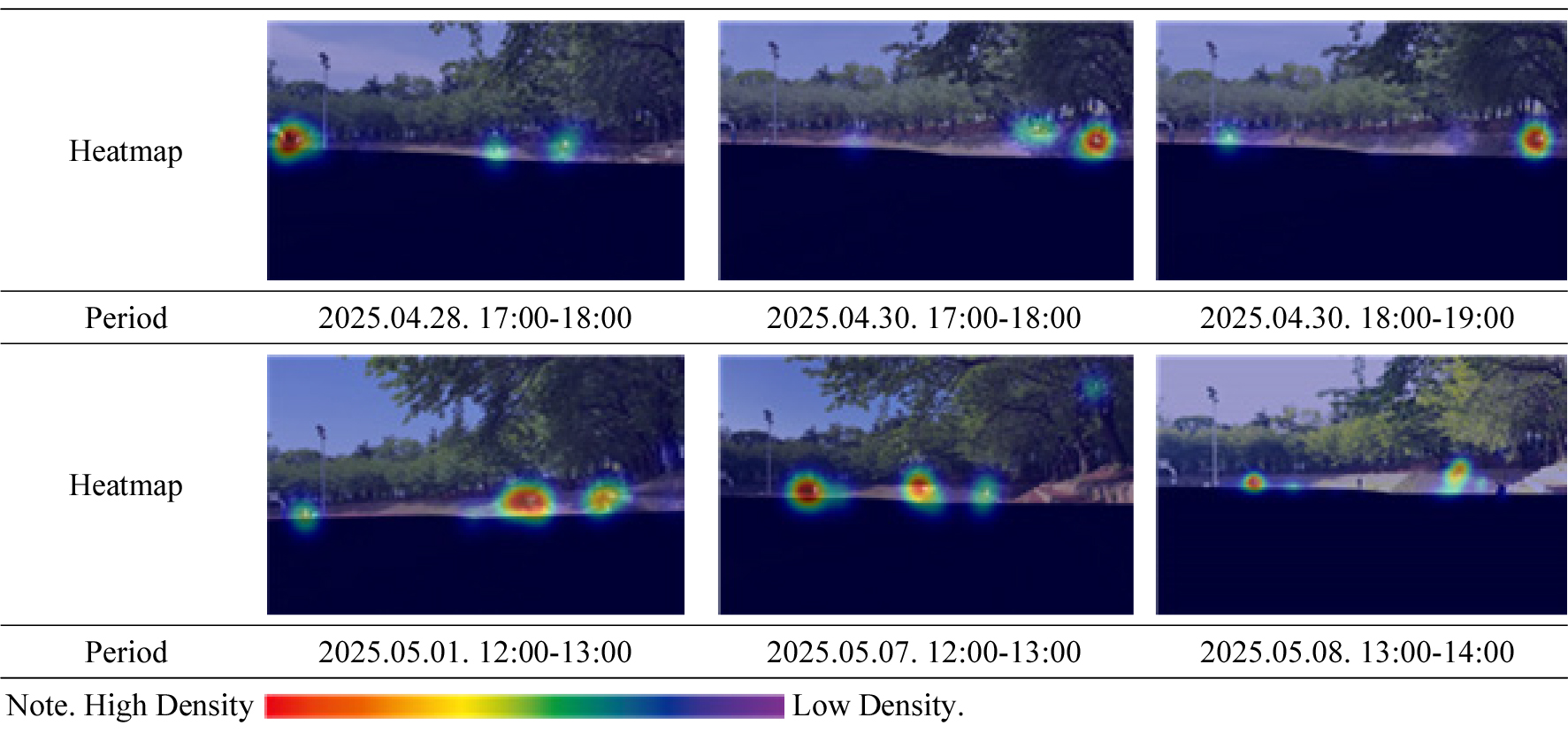
- This study aims to analyze the spatial structure of a university Athletic field and propose design improvements to enhance its utilization. A spatial model was developed using actual site drawings, and the Space Syntax method was applied to evaluate visual integration and connectivity of major access routes. In addition, YOLO-based object detection was employed to measure pedestrian volume along each route, and user surveys were conducted to collect satisfaction levels and dissatisfaction factors. The analysis revealed that the route with the highest pedestrian volume had the lowest visual integration and connectivity among the four main entrances, suggesting that factors beyond spatial configuration influence user choices, while routes with structurally unfavorable conditions offer greater potential for improvement. Survey results further indicated that physical problems such as smoking areas, unpaved sections, inconvenient stairs, and low visual openness negatively affected user experience. Based on these findings, design strategies were proposed, including improved visibility, pavement maintenance, relocation of smoking zones, and installation of nighttime lighting, integrated into a design collage to suggest feasible spatial interventions. This study provides a case that combines quantitative and qualitative analyses of how the spatial structure of a large-scale campus sports facility affects user behavior, and offers valuable insights for future planning and redesign of public sports facilities. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on Improving Campus Spaces for Physical Activity using AI-Based Analysis
-
Research Article
-
Postural Differences in Skin Temperature and Heat Flow from the Hand: Comparison of Standing, Supine, and Head-Down Tilt Positions
자세에 따른 피부온 및 손으로부터 방열량 차이: 선 자세, 누운 자세, 두부 하위 자세 비교
-
Suhyeon Yeom, Gyeong-Ri Kang, Sang-Hyun Roh, Joo-Young Lee
염수현, 강경리, 노상현, 이주영
- This study aimed to investigate posture-related variations in skin temperature and hand heat dissipation under simulated microgravity conditions. Eight young males (24 …
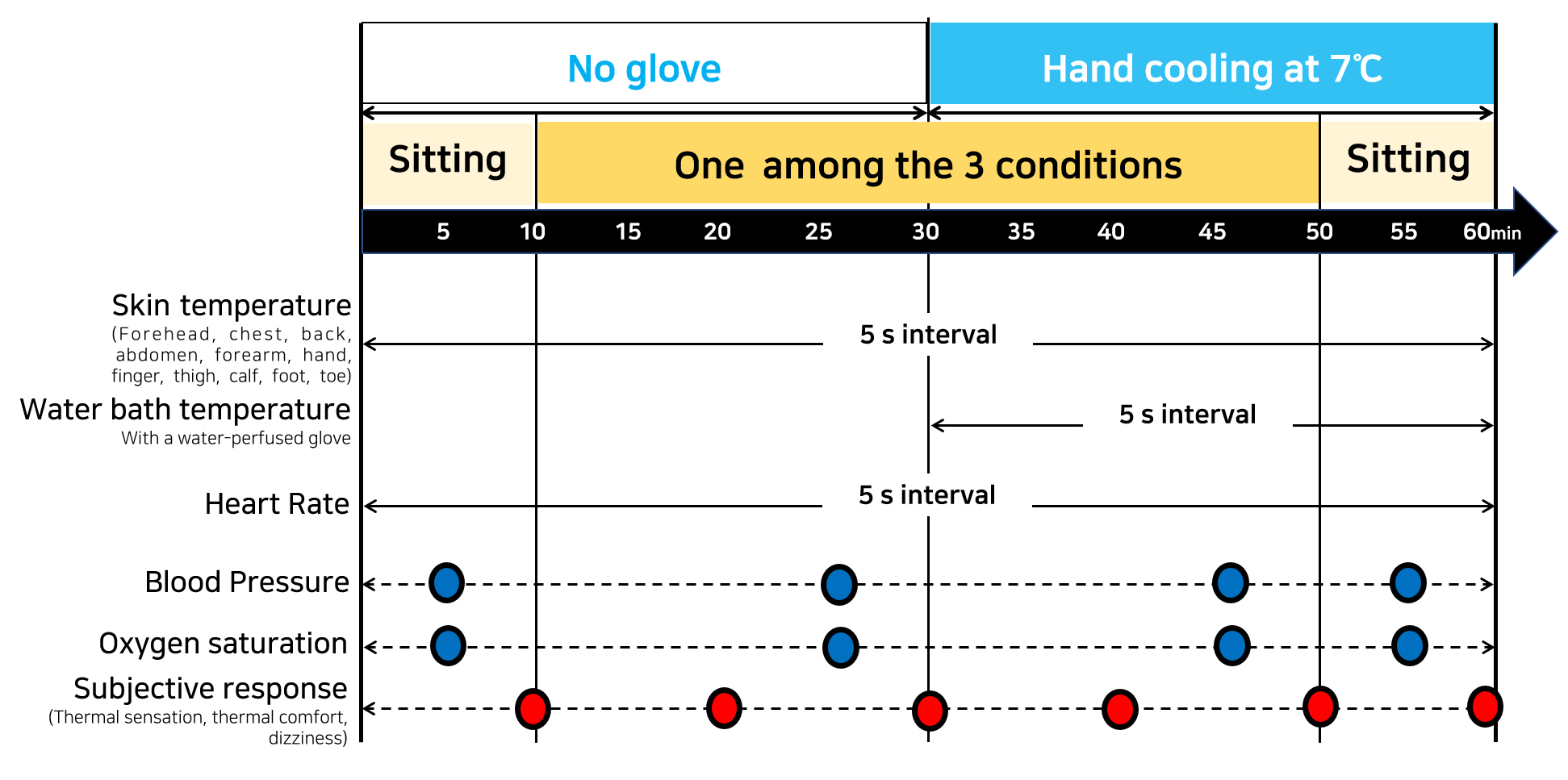
- This study aimed to investigate posture-related variations in skin temperature and hand heat dissipation under simulated microgravity conditions. Eight young males (24 ± 3 y) participated in three posture conditions: standing, supine, and 10° head-down tilt (HDT), which mimics a microgravity environment. Experiments were conducted in a climate chamber (24 ± 1°C, 60 ± 5%RH). A water-perfused glove (7°C circulating water) was used for the last 30 min during each 60-min trial to quantify hand heat extraction. Mean skin temperature showed no significant difference among the three posture conditions (32.8–32.9°C), but the decrease from resting to posture phases was greater in the supine than standing condition (p < 0.01). Trunk temperatures increased significantly during both supine and HDT conditions, whereas finger temperature dropped sharply after glove cooling, with a larger decline in the supine and HDT posture conditions (p < 0.05). Heart rate and blood pressure were significantly higher in the standing posture than in the two recumbent conditions (p < 0.05). Despite physiological redistribution of skin blood flow, hand heat extraction did not differ significantly among the postures (1.56 ± 1.00, 1.48 ± 0.88, and 1.69 ± 0.92 kcal·min-1, respectively). Thermal sensation, comfort, and dizziness scores showed no significant variation across the three conditions. These findings suggest that posture-induced changes in blood redistribution alter local skin temperature but have limited impact on overall hand cooling efficiency. The results provide fundamental insights into human thermoregulation under simulated microgravity, supporting the design of liquid-coolded garments for future manned space missions. - COLLAPSE
-
Postural Differences in Skin Temperature and Heat Flow from the Hand: Comparison of Standing, Supine, and Head-Down Tilt Positions
-
Research Article
-
Thermal Sensation and Thermal Comfort while Wearing Down-Padded Jackets with a Regional-Baffle Design in a Cold Environment
인체 부위별 Baffle 디자인을 적용한 겨울철 다운 재킷 착용 시 한서감과 온열쾌적감
-
Chanhyeok Kang, JuYoun Kwon, Syifa Salsabila, Ho-Joon Lee, Jae-Yeon Jung, Joo-Young Lee
강찬혁, 권주연, SalsabilaSyifa, 이호준, 정재연, 이주영
- This study investigated the effects of regional down insulation on thermal sensation, thermal comfort, and shivering responses during cold exposure while wearing …
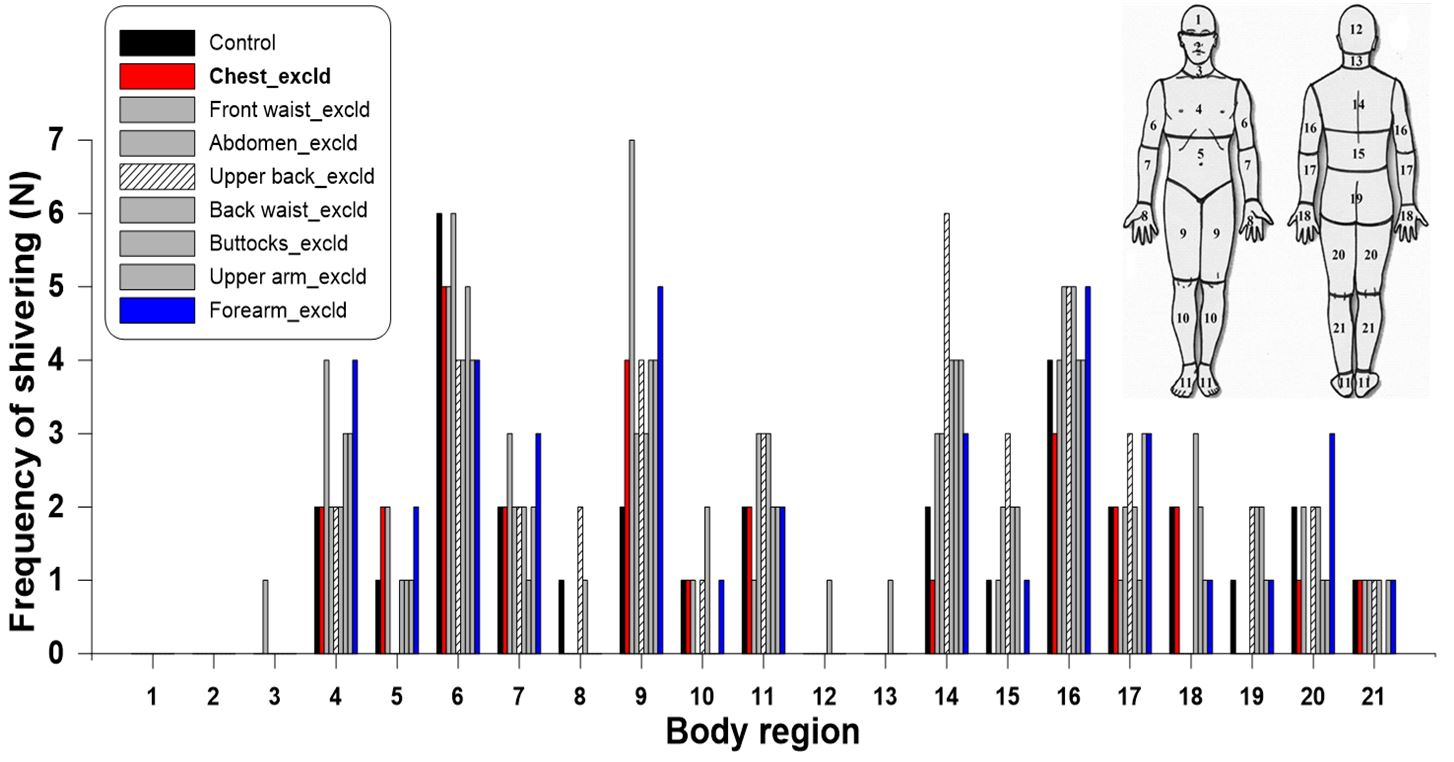
- This study investigated the effects of regional down insulation on thermal sensation, thermal comfort, and shivering responses during cold exposure while wearing a baffle-type padded jacket. Eight healthy young males (23.4 ± 2.5 y) participated in nine trials in a climate chamber set at −9.7 ± 1.0°C, each lasting 60 min in a seated posture. The experimental padded winter jacket was divided into eight compartments (chest, front waist, abdomen, upper back, lower back, hips, upper arms, and forearms), and insulation was selectively removed from one compartment per trial, with the fully filled jacket serving as the control. Whole-body and local thermal sensation and comfort were assessed every 10 min using standardized categorical scales, and shivering frequency and location were recorded. Removal of insulation from the chest, abdomen, or hips did not significantly affect whole-body thermal sensation or thermal comfort. In contrast, removing insulation from the upper back or upper arms significantly increased local cold sensation (p < 0.05) and reduced thermal comfort. Clothing insulation measured by a thermal manikin decreased only slightly (≤ 0.07 clo) when any single compartment was unfilled, suggesting minimal overall thermal impact. These results indicate that maintaining insulation at the upper back and upper arms is critical for preserving thermal sensation/comfort and reducing shivering, whereas partial insulation reduction at the chest or abdomen is possible without compromising overall thermal perception. The findings provide practical insights for designing energy-efficient winter jackets that minimize down usage while maintaining wearer comfort and supporting behavioral thermoregulation. - COLLAPSE
-
Thermal Sensation and Thermal Comfort while Wearing Down-Padded Jackets with a Regional-Baffle Design in a Cold Environment
-
Case Study
-
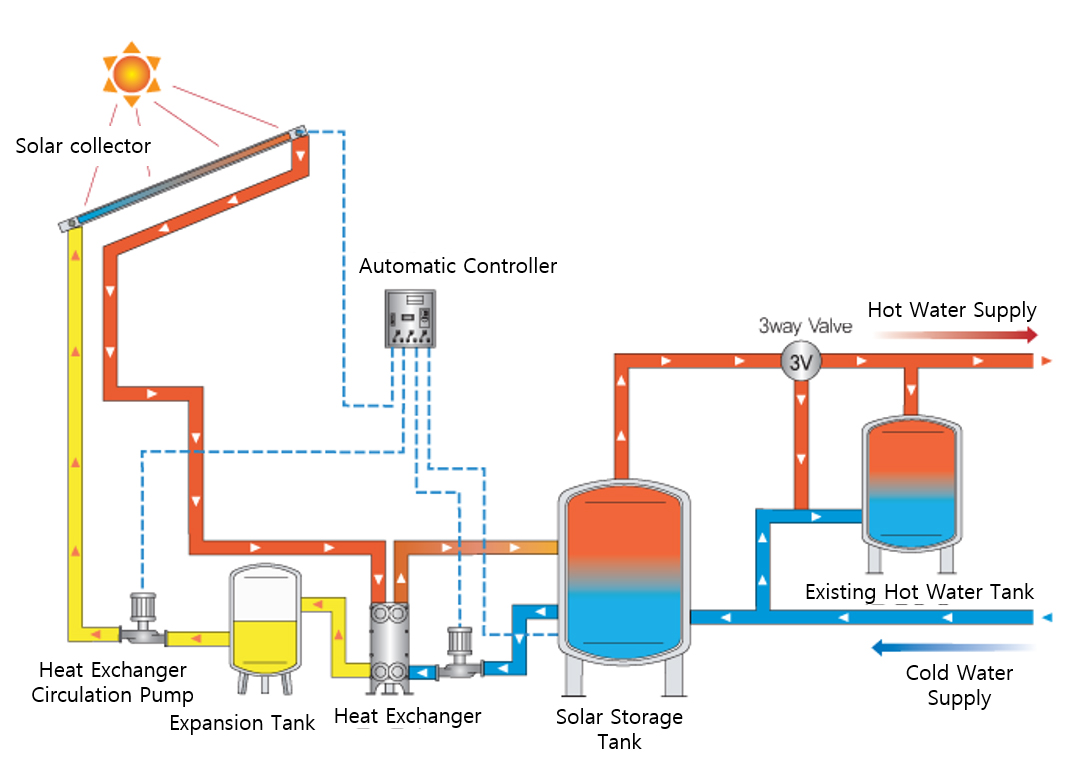
Case-Based Analysis for Establishing Economic Design Standards of Solar Hot Water System
태양열 급탕 시스템의 경제적 설계 기준 도출을 위한 사례 기반 분석
-
Doo-Sung Choi, Young-Ho Jung, Hung-Chan Jeon
최두성, 정용호, 전흥찬
- This study presents the appropriate Solar Fraction for solar hot water systems according to seasonal heat load distribution and hot water usage …
- This study presents the appropriate Solar Fraction for solar hot water systems according to seasonal heat load distribution and hot water usage patterns, based on case analyses of buildings with high domestic hot water demand where solar thermal systems have been applied. For this purpose, five types of buildings were selected and analyzed among apartment and lodging facilities that have relatively large collector areas and reflect seasonal variations in thermal load distribution. The analysis results indicate that, when both economic feasibility and system efficiency are considered, the optimal solar fraction is approximately 45–50% for buildings where the summer hot water load accounts for about 30–100% of the winter load, while buildings with relatively uniform year-round hot water loads show an optimal value of around 55%. - COLLAPSE
-
Case-Based Analysis for Establishing Economic Design Standards of Solar Hot Water System
-
Technical Notes

-
A Study on the Development of Core Technologies Based on the Analysis of Domestic and International Noise Barrier Research Trends
국내외 방음벽 연구 동향 분석을 통한 핵심 필요 기술 개발 방향에 관한 고찰
-
Jun-Oh Yeon, Soon-Seong Moon, Hee-Mo Goo, Wan-Ki Moon
연준오, 문순성, 구희모, 문완기
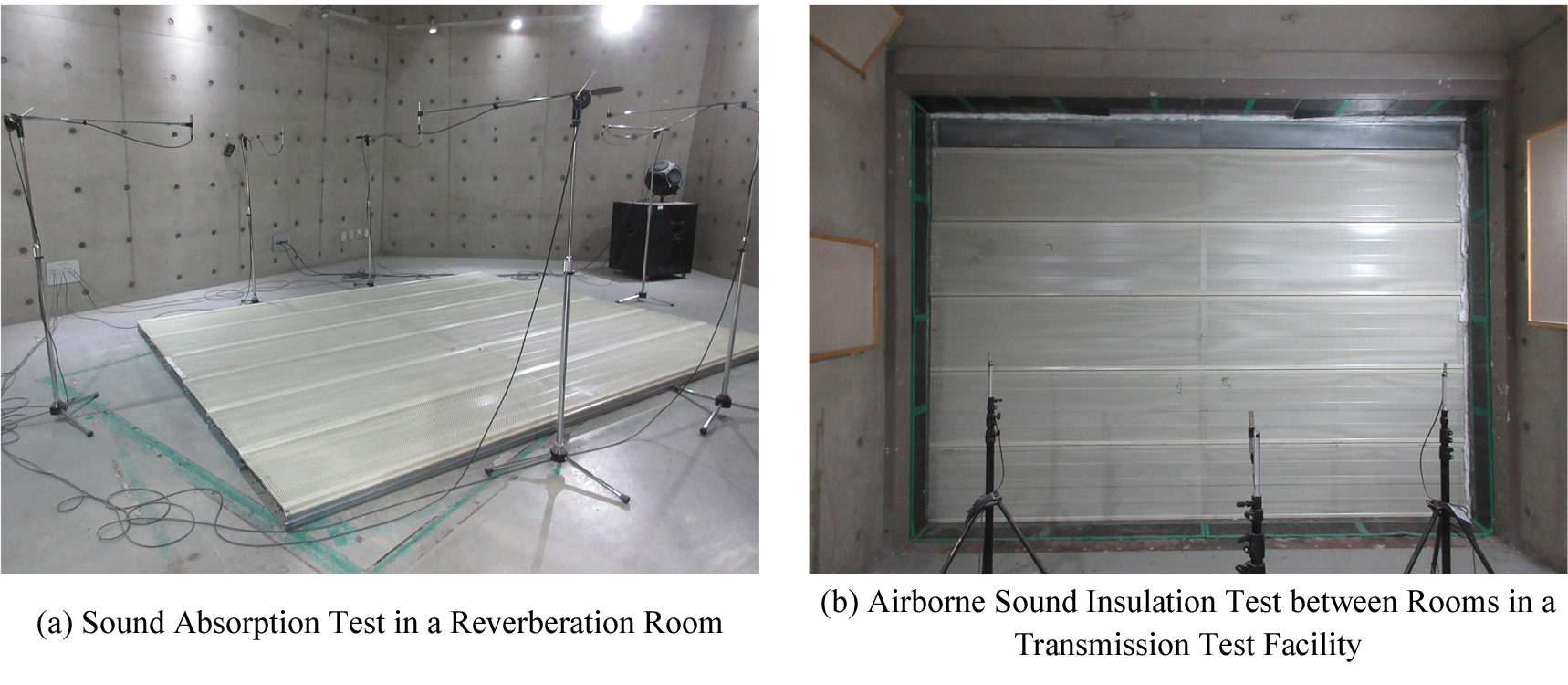
- Road traffic noise represents a major environmental challenge in densely populated urban areas, prompting the widespread implementation of noise barriers and tunnels …
- Road traffic noise represents a major environmental challenge in densely populated urban areas, prompting the widespread implementation of noise barriers and tunnels as key mitigation measures. This study provides a comprehensive review of domestic and international regulations, classification systems, and recent research trends related to these noise control structures. Noise barriers are generally categorized as sound-absorbing, reflective, or tunnel-type, each exhibiting distinct material compositions, structural features, and performance characteristics. Recent Korean studies have emphasized multifunctional approaches, such as improved sound absorption standards, integration of photovoltaic modules into transparent barriers, and hybrid systems combining noise reduction with dust filtration and active noise control. In contrast, international research primarily focuses on standardized performance evaluation, structural safety, and eco-friendly design principles. Representative examples include field tests of aluminum foam panels, the application of tilting mechanisms to mitigate wind loads, and the establishment of comprehensive design and management guidelines in Europe. While Korea demonstrates technological innovation and multifunctional development, challenges remain in large-scale validation, long-term durability, and fire safety—particularly for tunnel-type barriers. International efforts, though systematic and standardized, are relatively conservative in adopting multifunctional systems. Notably, fire safety considerations are insufficiently addressed in both domestic and international contexts. Future research should therefore integrate multifunctionality with structural resilience by prioritizing non-combustible materials, fire-resistant designs, and sustainable long-term performance, thereby advancing noise barriers as safe, durable, and sustainable components of urban infrastructure. - COLLAPSE
-
A Study on the Development of Core Technologies Based on the Analysis of Domestic and International Noise Barrier Research Trends
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of The Korean Society of Living Environmental System
Journal of The Korean Society of Living Environmental System
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of The Korean Society of Living Environmental System
Journal of The Korean Society of Living Environmental System












